BIRP notes

BIRP notes … Let’s face it, no therapist likes writing progress notes. But it is also one of the most important acts that a clinician does. Clinical notes act as a guide for treatment and evidence that it is occurring as planned. A lot of therapists just scribble down whatever is on their mind. But it is desirable to have a proven template. That is where BIRP notes come in.
Summary
- BIRP notes, organized into Behavior, Intervention, Response, and Plan, they help therapists clearly document client progress and their own clinical actions. Download my free BIRP note template.
- Unlike SOAP notes, BIRP notes highlight what the therapist did in session and how the client responded, making them ideal for tracking the effectiveness of interventions.
- BIRP notes demonstrate alignment with treatment plans and measurable progress, which insurers appreciate when reviewing claims.
- BIRP notes are especially helpful for new clinicians and clinical supervisors, as they support consistent treatment goal monitoring and therapist development.
- By leveraging an EHR like TheraPlatform for efficient documentation and claim submission, therapists can tackle billing and notes with ease.
Streamline your practice with One EHR
- Scheduling
- Flexible notes
- Template library
- Billing & payments
- Insurance claims
- Client portal
- Telehealth
- E-fax

What are BIRP notes?
BIRP notes are used to help clinicians organize their thoughts into four sections: behavior, intervention, response, and plan. They are meant to provide an efficient way to measure both a client’s progress and the clinician’s involvement. They can be used in almost all behavioral health settings. Let’s examine the BIRP format in greater detail.
How to write a BIRP note?
Here is the breakdown of how and what to document under each section of the BIRP note.
Behavior section of BIRP note
The behavior section of the BIRP note is used to relay the client’s presenting problems as well as their behavior in response to the last session. This is the section where you answer overall questions about their progress. Behavior is often split into two types of observations, objective and subjective.
Subjective observations are those provided from the client’s point of view. This is information that the client presents to the therapist during the session, including their exact words. For example, a client telling their therapist that they felt horrible because they ate three pints of ice cream in response to a romantic rejection would be a subjective observation.
Objective observations are provided by the clinician. These may be comments about a client’s physical appearance, their perceived emotional state, or their attitudes toward therapy. For example, a therapist might note a client did not complete their homework or seemed exhausted.
Practice Management + EHR + Telehealth
Mange more in less time in your practice with TheraPlatform
.
Intervention section of BIRP note
If the behavior section is all about the client, the intervention section is focused on the actions of the therapist. Specifically, it asks what the clinician is doing to help the client reach their goals. This includes the specific interventions that a therapist used in session.
Linking the therapist’s actions with the objectives in the client’s treatment plan is critical. Let’s say, for instance, the client has a goal to sleep 6-8 hours a night because they tend not to prioritize sleep. An appropriate intervention for the week might sound something like this: “the therapist tasked the client with the goal of turning off all screens an hour before sleep.”
Because it is all about interventions, the language in your notes should be action oriented. For example, the therapist “encouraged” the client to confront their fears. Or the therapist “modeled” deep breathing.
It is also helpful for people reading your notes to know the therapist’s theoretical approach. Let them know that your intervention is based on cognitive-behavioral or psychodynamic principles, for instance.
Response section of BIRP note
The response section of BIRP notes records the client reactions to the clinician’s interventions. Although we want all interventions to help, sometimes they just don’t work. Thus, responses can be both positive and negative. It is important to be as specific as possible. Quotes often help the reader know exactly how the client reacted. For example, the client may say “I couldn’t turn off my screens before bed because I kept getting messages from work”. In this case, the client provided valuable information that another type of intervention may be needed.
Reactions to therapy as a whole are also recorded here. Comments like “I just don’t feel like this is working” or “that technique was really helpful” provide a wealth of information. If you are unsure about a client’s progress, don’t be afraid to ask the client how they feel therapy is going. Between the behavior and response sections, you will get a feel for how to tailor the therapy in a way that is most effective for the client.
Plan section of BIRP note
The plan is the final section of the BIRP note. You will develop your plan based upon the client’s behaviors and responses from their session. The plan should be completed from both a short-term and a long-term perspective.
In the short-term, a therapist will want to note the time and date of the next scheduled appointment. They will talk about what homework was given and the focus of the next session. For example, “next session the therapist will introduce the client to additional techniques to promote sleep”.
In the long-term, you will need to determine if what happened in the session necessitates any changes to the treatment plan. Maybe, for instance, the client disclosed something that requires immediate attention and a new goal. You might write “client reports they are having suicidal thoughts but no intent” and then describe the new goal to address this concern. Whatever the case, it is crucial to note any changes and explain your reasoning for the change.
Watch this video to learn how to simplify note taking
→ Start My Free Trial
→ Start My Free Trial
BIRP notes vs SOAP notes
SOAP (subjective, objectives, assessment, plan) notes are used in many clinical settings as a template for progress notes. They overlap considerably with BIRP notes but they have a slightly different emphasis. Put simply, SOAP notes have an assessment section and BIRP notes do not. This does not mean that the therapist does not assess their clients when they use BIRP notes but it is not as explicitly stated.
BIRP notes are more focused on what the therapist is doing and the response to those specific interventions. It looks more at the process of therapy and the client’s reactions. In short, it focuses more on the effectiveness of the therapy rather than the state of the client.
One of the strengths of BIRP notes is that they keep the therapist and the client focused on their treatment goals. This puts pressure on the therapist to keep the therapy moving forward and to develop the most effective interventions. Because SOAP notes (and others) focus more on client assessment, there is more of a risk for stagnation in the therapy process.
BIRP notes can be used in any therapeutic situation, but they are especially useful for studying therapist behavior and its effectiveness. This can be very helpful for students and new therapists who may just be learning how to conduct therapy. In a setting that trains new clinicians, for example, BIRP notes are a constructive tool to examine therapist strengths and weaknesses.
BIRP note examples
The following are two examples of progress notes written using the BIRP note format for clients with common psychiatric disorders. One is for a client with generalized anxiety disorder. The other is for a client with major depressive disorder.
Generalized anxiety BIRP note example
- Behavior: Client reported sleeping only 3-4 hours a night due to worries. Avoiding social interactions because of fear of judgments. Client said, “I would rather stay home than be scorned by other people”. Looked agitated, tired, shaking leg. Appears to be ruminating about lack of friends but afraid to do anything about it.
- Intervention: Taught relaxation techniques, including deep abdominal breathing. Went over the concept of “worry time” with client to aid in sleep. Discussed scheduling a prosocial activity for this week. Asked client “what is the worst that can happen?” if they go outside their comfort zone.
- Response: Expressed desire to try something new but noted some reluctance. Does not seem motivated to follow through. Didn’t complete homework from last time.
- Plan: Meet next week. Client will practice relaxation daily. Will practice “worry time”every night before bedtime. Client will perform scheduled social activity. Next week client will be taught progressive muscle relaxation and review anxious thinking regarding social situations.
Major depressive disorder BIRP note example
- Behavior: Client said they were waking up in the middle of the night and having difficulty returning to sleep. Difficulty getting out of bed in the morning. Missed work once because of it. Reported that they felt “sad most of the time” and “alone”. Looked tired and lethargic. Therapist noted slumped shoulders and self-defeating comments. Client appears to be gaining weight. Fresh cut marks observed on upper arm.
- Intervention: Conducted cognitive restructuring using completed thought record. Scheduled video contact with brother. Assessed for suicidality. Discussed alternatives to cutting behavior and crisis management procedures.
- Response: Seemed embarrassed when confronted with cutting behavior but did discuss it openly. Despite cutting, did not voice any suicidal ideation. Completed homework from last time. Seems engaged with therapy but not with the rest of life.
- Plan: Meet next week. Phone consultation available if necessary. Cutting behavior and thoughts of self-harm will be revisited next week. Client will complete thought record daily. Client is asked to follow-through on contact with brother.
Free Resources for Therapists
Click below and help yourself to peer-created resources:

Tips on using BIRP notes
Here are some tips and thoughts for making the most out of BIRP notes:
Be detailed but not verbose in your BIRP
BIRP notes are meant to be efficient. You want to get your point across without making someone read unnecessary filler. But, since these are official notes of record, you don’t want to leave out anything important. Always keep in mind that these notes could be used in court, if necessary. In other words, be concise. A few relevant lines per section is usually all you will need.
Don’t rush your BIRP notes
At the same time, don’t rush in completing your BIRP notes. If you ask clinicians their favorite part about treatment, almost no one is going to say progress notes. They just aren’t that much fun. Therefore, therapists often act carelessly when completing them. BIRP notes are susceptible to rushing because they have an easy-to-complete template and they encourage conciseness. Just keep in mind that these notes are important. It won’t take much extra time to do it right.
Know your audience
Always keep in mind that clinical notes are not just for you. Yes, you may want to review them but they will stick with the client long after they are done seeing you. Your immediate audience may be a supervisor or another professional but it can be anyone who will review your client’s record at any point in their lives. Think about who might read them and make sure they sound appropriate for different audiences.
Use quotes when possible in your BIRP notes
Client quotes are highly encouraged in the behavior and response sections of BIRP notes. Why? Because there is no risk of the clinician getting it wrong. When therapists paraphrase in notes, they often change the meaning and interpretation of what the client said. A quote doesn’t allow that. Besides, everything is more convincing when it comes directly from the client’s mouth.
Insurance companies love BIRP notes
Clinicians and insurance companies don’t always get along. Insurance companies want the quickest treatment possible to help keep costs down. Therapists, in contrast, want to do whatever is best for the client, even if that means more sessions than insurance would prefer. Something both sides can agree upon, however, are BIRP notes.
Insurance companies love them because they help professionals focus on their treatment plans and assist clients in meeting their objectives. In other words, they help therapists be most efficient. And clinicians like them because they provide a simple way to show insurance companies that they are doing right by the client and not just adding irrelevant sessions to make a quick buck. If insurance companies begin to question your treatment progress, you can just show them your BIRP notes to put them at ease. Moral of the story: if you are a practitioner that works a lot with insurance, you may want to use BIRP notes to reduce the anxiety that frequently occurs when working with insurance companies.
BIRP notes are an efficient way to keep track of client progress in a behavioral health setting. They provide a format that helps clinicians stay on track in meeting the client’s objectives. And they are especially useful as a tool to examine the effectiveness of therapist interventions.
Additional tools to help with and progress monitoring
Therapists can also take advantage of EHRs (such as TheraPlatform) that offer integrations with Wiley treatment planners to ensure consistent data collection on progress from session to session. The best part about partnering with a modern EHR is the time you save on formulating the actual notes.
What is Wiley Treatment Planner?
Wiley Treatment Planner is a widely used clinical resource designed to help mental health professionals and other therapists efficiently create treatment plans for their clients. In addition to treatment plans, the company also provides prewritten therapy notes for some diagnostic codes. It is part of the "PracticePlanners" series published by Wiley.
Features of Wiley Treatment Planner includes:
- Prewritten, evidence-based treatment goals, objectives, and interventions
- Treatment planners tailored to specific populations and problems, including adults, children, adolescents, couples, families, addictions, and more
- Alignment with the diagnostic criteria from the DSM-5 and ICD-10
- Prewritten therapy notes
Is there an online version of Wiley Treatment Planner and how can I get the Wiley Treatment Planner?
Wiley Treatment Planner company partnered with a select number of EHRs for mental health providers to make treatment planners available online. TheraPlatform’s EHR offers the Wiley Treatment Planner as an add-on for both assessment and treatment plans and therapy notes, such as BIRP notes. You can edit prewritten notes and add your own with any therapy template on TheraPlatform.
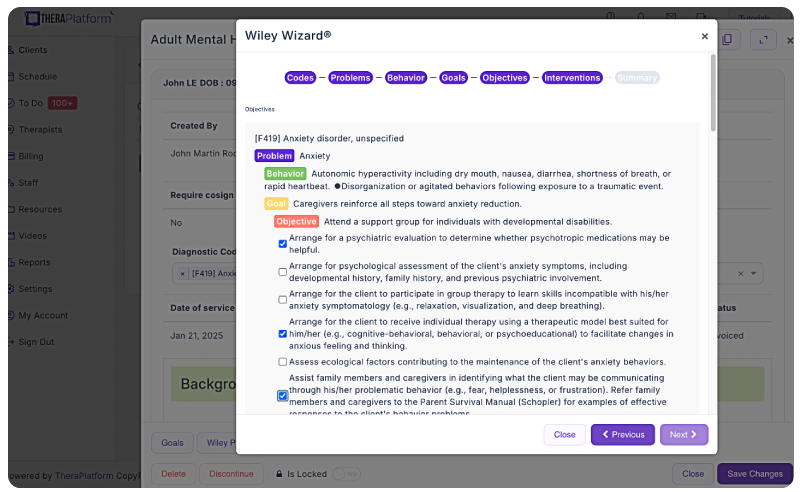
Improving notes with EHR software
EHR software and practice management tools, such as TheraPlatform, offer numerous advantages in creating accurate, efficient, and organized notes.
Top 7 benefits of using EHR for notes management
Manually writing and storing notes can be cumbersome for many therapists. That process can be further exacerbated by simple document requests that include locating, faxing or scanning documents.
Features like customizable templates, secure storage, easy sharing, duplication, electronic signatures, and efax integration, streamline the note process, optimizing therapy documentation and workflows.
- Consistent notes with template library: EHRs equipped with a library of note templates enable therapists to create standardized and concise notes quickly. This feature ensures consistency across notes, making it easier to review client progress. Additionally, EHRs provide centralized storage and management of notes, enhancing accessibility and organization.
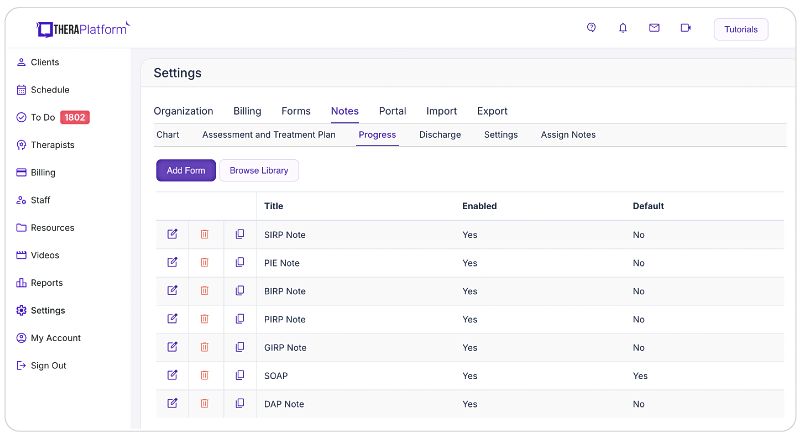
- Customizable notes: Not all EHRs offer customizable note templates tailored to therapists' unique needs. However, with a robust and user-friendly note template builder, therapists can customize note templates to align with their preferred note-taking style. This flexibility allows for efficient data entry, whether therapists prefer separating sections or using a single note field or checkboxes for mental status or techniques.
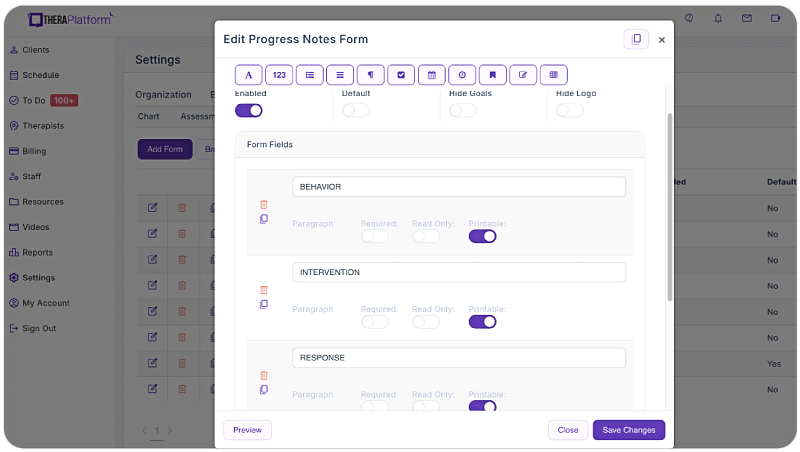
- HIPAA-compliant note storage: EHRs prioritize data security by implementing bank-level encryption to safeguard notes and other client information. TheraPlatform, for instance, ensures HIPAA compliance by offering signed, legally-binding Business Associate Agreements to protect Protected Health Information (PHI) between compliant entities.
- Seamless note sharing with clients: Clients may request access to their notes to better understand their treatment or keep them for record-keeping purposes. Using an EHR, therapists can securely share notes with clients, saving time compared to paper-based practices. TheraPlatform, a HIPAA-compliant EHR for therapists, facilitates secure note sharing with clients.

- Duplicate notes: In cases where the data remains the same across multiple sessions, duplicating notes can save time. This feature is particularly useful when clients exhibit repetitive behaviors or show minimal progress, allowing therapists to refer back to previous notes for accurate documentation.
- Client signatures made easy: EHRs streamline the process of requesting client signatures. TheraPlatform's Pro and Pro Plus plans enable therapists to request electronic signatures directly on notes. Clients can conveniently download and print the documents requiring their signatures.
- Easier faxing: TheraPlatform offers efax integration as an add-on feature, eliminating the need for toggling between multiple services. This integrated solution allows therapists to send and receive documents, including notes, via fax directly from TheraPlatform. Additionally, received faxes can be easily filed under the respective client's charts.
By leveraging the capabilities of EHR software like TheraPlatform, therapists can enhance the accuracy, efficiency, and accessibility of their notes, allowing them more time to enhance client care.
Streamline your practice with One EHR
- Scheduling
- Flexible notes
- Template library
- Billing & payments
- Insurance claims
- Client portal
- Telehealth
- E-fax

Resources
TheraPlatform is an all-in-one EHR, practice management, and teletherapy software built for therapists to help them save time on admin tasks. It offers a 30-day risk-free trial with no credit card required and supports mental and behavioral health, SLPs, OTs, and PTs in group and solo practices.
More resources
- SOAP notes
- SOAP notes worksheets
- Suicidal ideation ICD-10
- Wiley treatment planners
- Therapy resources and worksheets
- Therapy private practice courses
- Ultimate teletherapy ebook
- The Ultimate Insurance Billing Guide for Therapists
- The Ultimate Guide to Starting a Private Therapy Practice



