PIE notes

PIE notes are one of several mental health therapy documentation approaches with notes playing a pivotal role in tracking client progress, ensuring compliance, and facilitating seamless communication among care providers. Among the various note-taking formats, PIE notes have emerged as a concise and effective method for capturing the essence of each therapeutic session.
Summary
- PIE stands for Problem, Intervention, and Evaluation—a concise and efficient documentation format that helps therapists clearly track client concerns, therapeutic approaches used, and outcomes from session to session.
- This format supports evidence-based practice by encouraging therapists to document not just what was done, but why it was chosen, and how it aligns with client goals and current research. Download our free PIE note template.
- While SOAP notes are more comprehensive, PIE notes offer a streamlined alternative ideal for outpatient or private practice settings where brevity and clarity are prioritized.
- Using EMR platforms like TheraPlatform can enhance the PIE note process by offering customizable templates, secure storage, and easy sharing—saving time and improving workflow for mental health professionals.
Streamline your practice with One EHR
- Scheduling
- Flexible notes
- Template library
- Billing & payments
- Insurance claims
- Client portal
- Telehealth
- E-fax

What does PIE stand for in mental health?
PIE notes, an acronym for Problem, Intervention, and Evaluation, provide a structured framework for therapists to document their sessions efficiently. This approach not only streamlines the documentation process but also ensures that essential information is captured clearly and organized.
A snapshot of PIE notes
At their core, PIE notes are a method of clinical documentation that condenses the critical elements of a therapy session into three distinct sections. By adhering to this format, therapists can effectively communicate client progress, interventions employed, and treatment outcomes to other healthcare professionals involved in the client's care.
Example of PIE Notes 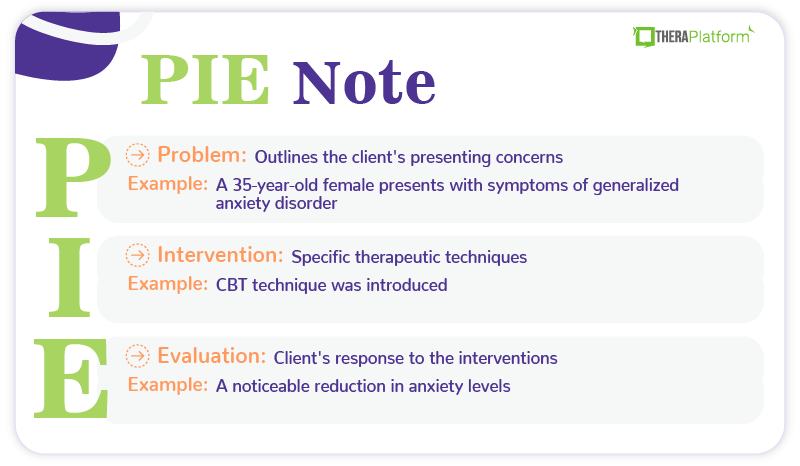
→ Download My Free PIE Note Template

Decoding the PIE acronym
The PIE acronym serves as a mnemonic device, guiding therapists through the three essential components of their notes:
- P (Problem): Outlines the client's presenting concerns, symptoms, and treatment goals
- I (Intervention): Specific therapeutic techniques and strategies employed to address the client's problems
- E (Evaluation): The final section evaluates the client's response to the interventions and tracks their progress over time.
The significance of PIE notes in mental health therapy
Implementing PIE notes in mental health therapy offers numerous advantages. Not only do they facilitate clear and concise communication among care providers, but they also ensure that critical information is readily available for review and analysis. By maintaining a consistent documentation format, therapists can streamline their note-taking process, freeing up valuable time to focus on delivering high-quality care to their clients.
Practice Management + EHR + Telehealth
Manage more in less time in your practice with TheraPlatform
Dissecting the PIE note: A closer look
To fully appreciate the power of PIE notes, it is essential to understand the nuances of each component and how they contribute to the overall effectiveness of this documentation method.
The problem section of PIE notes: Identifying client concerns
The Problem section serves as the foundation of the PIE note, capturing the client's presenting issues, symptoms, and treatment goals. In this section, therapists should strive to articulate the client's concerns clearly and concisely, utilizing standardized diagnostic criteria and assessment tools when appropriate.
Effective problem identification involves:
- Documenting the client's self-reported concerns and symptoms
- Incorporating observations and assessments from the therapist's perspective
- Outlining specific treatment objectives and desired outcomes
By establishing a comprehensive understanding of the client's problems, therapists can tailor their interventions and track progress more effectively.
The intervention section of PIE notes: Documenting therapeutic strategies
The Intervention section is dedicated to documenting the specific therapeutic techniques and strategies employed during the session. This section should not only describe the interventions but also provide a rationale for their selection and implementation.
Effective intervention documentation involves:
- Detailing the specific therapeutic modalities and techniques utilized
- Explaining the rationale behind the chosen interventions
- Incorporating evidence-based practices and client preferences
By thoroughly documenting the interventions, therapists create a valuable record that can be referenced and analyzed to inform future treatment decisions.
Justifying intervention selection
In addition to describing the interventions, it is crucial to document the rationale behind their selection. This not only demonstrates the therapist's clinical reasoning but also helps ensure that interventions are tailored to the client's unique needs and preferences.
Factors to consider when justifying intervention selection include:
- Alignment with the client's presenting concerns and treatment goals
- Incorporation of evidence-based practices and empirically supported techniques
- Consideration of the client's cultural background, values, and preferences
By clearly articulating the rationale behind intervention selection, therapists can demonstrate their commitment to providing client-centered care and facilitate a deeper understanding of the therapeutic process among other care providers.
Integrating evidence-based practices
In the field of mental health therapy, it is essential to incorporate evidence-based practices into intervention selection and implementation. Evidence-based practices are interventions that have been empirically validated through rigorous research and have demonstrated effectiveness in addressing specific mental health concerns.
When documenting interventions, therapists should:
- Reference relevant research studies or clinical guidelines
- Highlight the empirical support for the chosen interventions
- Discuss any modifications or adaptations made to align with the client's needs
By integrating evidence-based practices into their documentation, therapists not only enhance the credibility and effectiveness of their interventions but also contribute to the broader body of knowledge in the field of mental health therapy.
The evaluation section of PIE notes: Assessing client progress
The Evaluation section serves as a critical component of the PIE note, allowing therapists to monitor and assess the client's progress over time. In this section, therapists document the client's response to the interventions, noting any changes in symptoms, behaviors, or overall functioning.
Effective progress evaluation involves:
- Utilizing objective measures and outcome assessments
- Incorporating client self-report data and feedback
- Identifying areas for further monitoring or adjustment in the treatment plan
By consistently evaluating client progress, therapists can make informed decisions regarding the continuation, modification, or termination of specific interventions, ultimately enhancing the overall effectiveness of the treatment process.
Watch this video to learn how to save time on therapy notes
Navigating the nuances: PIE notes vs. SOAP notes
While PIE notes and SOAP (Subjective, Objective, Assessment, Plan) notes share some similarities, it is essential to understand the key differences between these documentation methods.
SOAP Notes: A comprehensive approach
SOAP notes are a widely recognized format in the healthcare industry, encompassing four distinct sections:
- S (Subjective): Captures the client's self-reported symptoms, concerns, and experiences.
- O (Objective): Observable data, such as assessment results and clinical observations.
- A (Assessment): Involves analyzing subjective and objective information to formulate a clinical impression or diagnosis.
- P (Plan): Outlines the proposed treatment plan, including interventions, referrals, and follow-up recommendations.
PIE notes: A focused approach
In contrast to the comprehensive nature of SOAP notes, PIE notes offer a more targeted and concise approach to documentation. While SOAP notes encompass a broader range of information, PIE notes specifically focus on the client's presenting problems, the interventions employed, and the evaluation of progress.
Choosing the appropriate format
The decision to use PIE notes or SOAP notes ultimately depends on the specific needs and preferences of the therapist and the clinical setting. SOAP notes may be more suitable for settings that require comprehensive documentation, such as medical facilities or multidisciplinary teams. On the other hand, PIE notes can be an excellent choice for therapists who value concision and efficiency in their documentation practices, particularly in private practice or outpatient settings.
Free Resources for Therapists
Click below and help yourself to peer-created resources:

Defining treatment goals and objectives
In addition to documenting client concerns and symptoms, the Problem section should also outline the specific treatment goals and objectives. These goals serve as a roadmap for the therapeutic journey, guiding the selection of interventions and providing a benchmark for evaluating progress.
Effective goal-setting involves:
- Collaborating with the client to identify realistic and achievable goals
- Ensuring that goals are specific, measurable, and time-bound
- Aligning goals with the client's values, preferences, and desired outcomes
By clearly defining treatment goals and objectives, therapists can maintain a focused and purposeful approach throughout the therapeutic process, increasing the likelihood of successful outcomes.
Assessing client progress
Assessing client progress involves carefully monitoring changes in the client's symptoms, behaviors, and overall functioning. Therapists should document both subjective and objective measures of progress, incorporating the client's self-report data as well as their own clinical observations.
Techniques for assessing client progress include:
- Administering standardized outcome measures or rating scales
- Conducting structured interviews or progress assessments
- Documenting observable changes in the client's behavior, mood, or functioning
By regularly assessing client progress, therapists can identify areas of improvement or stagnation, allowing for timely adjustments to the treatment plan and ensuring optimal outcomes.
Evaluating treatment effectiveness
In addition to assessing client progress, the Evaluation section should also address the overall effectiveness of the interventions employed. This evaluation can inform future treatment decisions and contribute to the ongoing refinement of therapeutic approaches.
Factors to consider when evaluating treatment effectiveness include:
- The degree to which the client's treatment goals have been achieved
- The client's level of engagement and adherence to the interventions
- The presence of any unanticipated challenges or barriers to progress
By critically evaluating treatment effectiveness, therapists can identify areas for improvement, explore alternative interventions, or reinforce successful approaches, ultimately enhancing the quality of care provided to their clients.
Incorporating client feedback
Client feedback is an invaluable component of the Evaluation section. By actively seeking and documenting the client's perspectives on the therapeutic process, therapists can gain valuable insights into the effectiveness of interventions, the therapeutic alliance, and areas for potential improvement.
Methods for incorporating client feedback include:
- Conducting structured feedback sessions or surveys
- Encouraging open dialogue and reflection during sessions
- Documenting the client's self-reported experiences and perceptions
By actively involving clients in the evaluation process, therapists not only foster a collaborative therapeutic relationship but also ensure that the treatment plan remains client-centered and responsive to the client's evolving needs and preferences.
PIE note example mental health
To further illustrate the practical application of PIE notes, let's explore two examples from different therapeutic contexts.
Example 1: Individual Therapy for Anxiety Disorder
Problem: The client, a 35-year-old female, presents with symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder, including excessive worry, restlessness, and difficulty concentrating. The client reports experiencing these symptoms for several months, which have significantly impacted her daily functioning and relationships. The primary treatment goal is to develop effective coping strategies for managing anxiety and improving overall well-being.
Intervention: During the session, the therapist introduced the client to cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) techniques, including psychoeducation on the cognitive model of anxiety and cognitive restructuring exercises. The client learned to identify and challenge negative thought patterns contributing to her anxiety. Additionally, the therapist guided the client through progressive muscle relaxation exercises to manage physiological symptoms of anxiety.
Evaluation: The client actively engaged in the CBT interventions and reported a noticeable reduction in anxiety levels during the session. She expressed a willingness to practice cognitive restructuring and relaxation techniques between sessions. The therapist will continue to monitor the client's progress and adjust the treatment plan as needed based on the client's response to the interventions.
Example 2: Couple's therapy for communication issues
Problem: A married couple in their early 40s seeks therapy to address ongoing communication difficulties and conflicts within their relationship. Both partners report feeling misunderstood and unheard, leading to frequent arguments and emotional distance. The primary treatment goal is to improve communication patterns and enhance emotional intimacy within the relationship.
Intervention: During the session, the therapist utilized the Gottman Method, an evidence-based approach to couple's therapy. The therapist guided the couple through active listening exercises, teaching them to express their needs and perspectives more effectively. Additionally, the couple practiced conflict resolution strategies, such as using "I" statements and taking breaks when necessary to prevent escalation.
Evaluation: Both partners demonstrated a willingness to engage in the communication exercises and expressed a desire to continue practicing the techniques at home. The therapist observed a noticeable improvement in the couple's ability to communicate without defensiveness or criticism. Moving forward, the therapist will continue to reinforce effective communication strategies and address any underlying issues contributing to the couple's conflicts.
Embracing best practices in PIE note documentation
While PIE notes offer a concise and effective approach to therapy documentation, adhering to best practices is essential to ensure accuracy, professionalism, and compliance with legal and ethical guidelines.
Ensuring accuracy and clarity
Accurate and clear documentation is paramount in the field of mental health therapy. Therapists should strive to document information in a precise and objective manner, avoiding subjective interpretations or speculative statements.
Best practices for ensuring accuracy and clarity include:
- Using specific and descriptive language
- Avoiding abbreviations or jargon that may be unclear to other care providers
- Proofreading notes for grammatical errors or inconsistencies
- Maintaining a professional and objective tone throughout the documentation
By prioritizing accuracy and clarity, therapists can enhance the credibility and usefulness of their PIE notes, facilitating effective communication and collaboration among care providers.
Adhering to legal and ethical guidelines
Mental health documentation is subject to various legal and ethical guidelines, including those related to client confidentiality and privacy. Therapists must ensure that their PIE notes comply with relevant regulations and professional standards.
Key considerations for adhering to legal and ethical guidelines include:
- Maintaining client confidentiality by avoiding the use of identifying information
- Storing and securing documentation in a HIPAA-compliant manner
- Obtaining appropriate consent and authorization from clients for documentation purposes
- Adhering to professional codes of ethics and standards of practice
By prioritizing legal and ethical compliance, therapists can protect client rights, maintain trust, and uphold the highest standards of professional conduct within the mental health field.
Incorporating client feedback and self-report data
Incorporating client feedback and self-report data into PIE notes can enhance the accuracy and client-centered nature of the documentation. By actively involving clients in the documentation process, therapists can gain valuable insights and ensure that the notes accurately reflect the client's experiences and perspectives.
Strategies for incorporating client feedback and self-report data include:
- Encouraging clients to review and provide feedback on session notes
- Incorporating direct quotes or narratives from the client into the documentation
- Utilizing client-completed assessments or rating scales as part of the evaluation process
By embracing a collaborative approach to documentation, therapists can foster a stronger therapeutic alliance, enhance client engagement, and ensure that the PIE notes accurately capture the client's journey toward improved mental health and well-being.
How can an EMR software can help with PIE notes?
EMR software, such as TheraPlatform, offers significant advantages in creating efficient, adaptable, and precise PIE notes for mental health therapists. The key is reducing the amount of time needed for creating, storing/managing and sharing notes through the use of intuitive features.
How to streamline the PIE notes process
The process around PIE notes typically involves creation, storage/access and sharing.
An EMR like TheraPlatform can minimize the amount of administrative burden associated with these steps. Let’s take a look at how TheraPlatform’s features helps streamline the PIE notes process.
PIE notes creation
Saving time on creating PIE notes for mental health therapy can be done in three ways.
- Using a template library: TheraPlatform's EMR provides built-in note templates, ensuring mental health therapists maintain conciseness and consistency in their documentation. Templates follow a standardized format, facilitating easy review. You can see an example of TheraPlatform’s built-in therapy note template in the screenshot below.
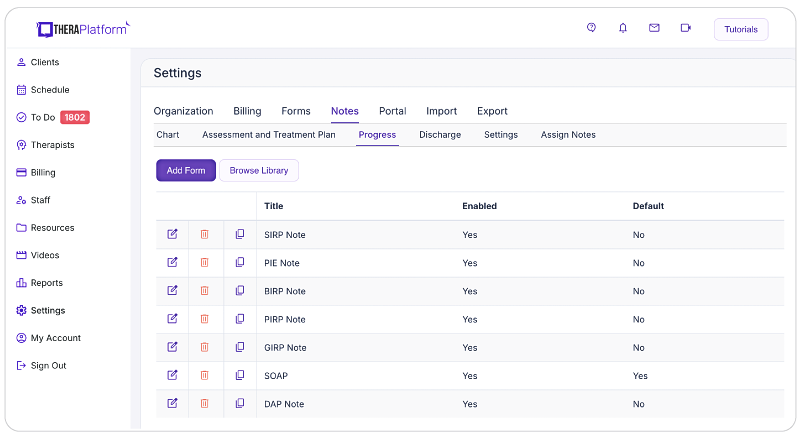
Screenshot of TheraPlatform’s built-in therapy note template library. Notes are one of dozens of types of templates that can be used as is or modified to meet the needs of a therapist in private practice
- Customizable note templates: Templates are a great foundation. In addition, TheraPlatform's EMR features a flexible note template builder, empowering mental therapists to customize PIE note templates according to their preferred documentation style. Whether you choose the traditional PIE format, a single narrative field, or the inclusion of checkboxes, the template builder provides efficiency and versatility without the need to completely modify an existing template.
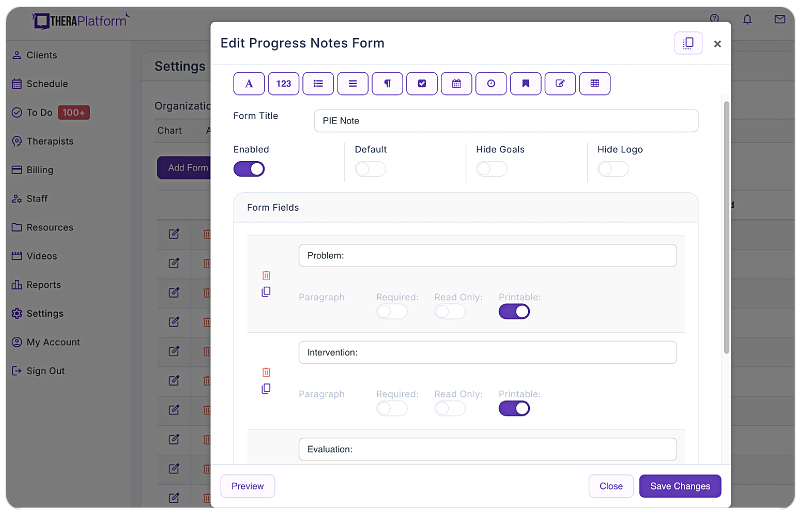
- Duplication: TheraPlatform's EMR enables mental health therapists to copy notes from previous sessions. This feature simplifies documenting recurring information or progress updates, allowing counselors or other mental health professionals to easily edit and expand upon the copied notes as necessary. No more writing the same information from scratch each and every time.

Mental health PIE notes and access
Once PIE notes are written, they should be organized in a way that is accessible and secure for the therapists. Oftentimes, manual methods provide more obstacles than efficiency. An EMR can help.
Storage
- HIPAA-Compliant and Secure Storage: Mental health notes contain sensitive client information, necessitating secure and HIPAA-compliant storage. TheraPlatform's EMR ensures adherence to HIPAA regulations, employing bank-level security measures to safeguard client data. Additionally, TheraPlatform provides signed Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) for further protection of Protected Health Information (PHI).
Sharing mental health PIE notes
In addition to therapist access, clients and other clinicians may also need to view mental health PIE notes. Having a seamless way to send, sign and receive notes in a secure environment helps ensure HIPAA compliance and provides a great client experience.
Sharing
- Secure sharing of mental health therapy notes: TheraPlatform's EMR eases secure sharing of mental health therapy notes with clients through a HIPAA-compliant client portal. Give clients convenient access to their notes for personal records or insurance audits while ensuring confidentiality and privacy.
- Electronic signatures: Through TheraPlatform’s Pro and Pro Plus plans, mental health therapists can request electronic signatures directly on notes. Clients can effortlessly download and print the signed documents, eliminating the need for physical signatures and paper-based processes.
- Integrated E-faxes: TheraPlatform's integration with efax services creates efficient communication and eliminates the need for separate platforms when sending or receiving PIE notes. With a simple click of a button, therapists can seamlessly send and receive faxes directly from TheraPlatform, reducing administrative tasks and enhancing efficiency.
Utilizing an EHR for mental health PIE note creation, storage and sharing is an easy decision and can save therapists time and frustration.
Additional tools and outcome measures to help with data collection and progress monitoring
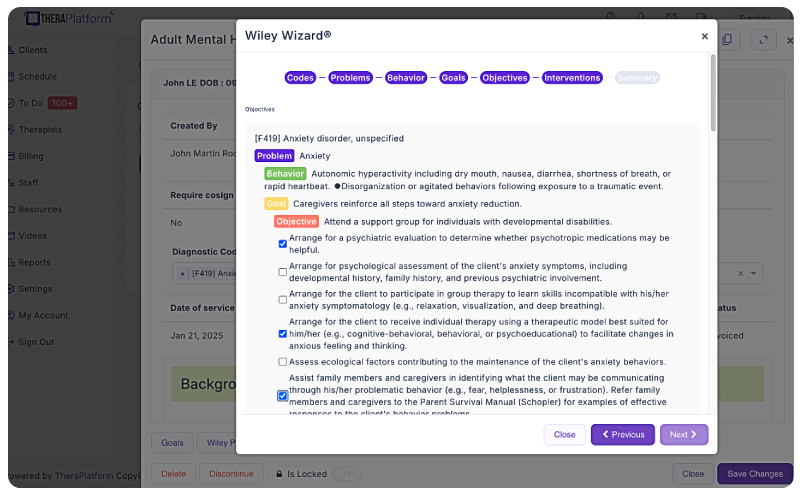
Therapists can also take advantage of EHRs (such as TheraPlatform) that offer integrations with Wiley treatment planners to ensure consistent data collection on progress from session to session. The best part about partnering with a modern EHR is the time you save on formulating the actual notes and scoring.
What is Wiley Treatment Planner?
Wiley Treatment Planner is a widely used clinical resource designed to help mental health professionals and other therapists efficiently create treatment plans for their clients. In addition to treatment plans, the company also provides prewritten therapy notes for some diagnostic codes. It is part of the "PracticePlanners" series published by Wiley.
Features of Wiley Treatment Planner includes:
- Prewritten, evidence-based treatment goals, objectives, and interventions
- Treatment planners tailored to specific populations and problems, including adults, children, adolescents, couples, families, addictions, and more
- Alignment with the diagnostic criteria from the DSM-5 and ICD-10
- Prewritten therapy notes
Is there an online version of Wiley Treatment Planner and how can I get the Wiley Treatment Planner?
Wiley Treatment Planner company partnered with a select number of EHRs for mental health providers to make treatment planners available online. TheraPlatform’s EHR offers the Wiley Treatment Planner as an add-on for both assessment and treatment plans and therapy notes, such as notes. You can edit prewritten notes and add your own with any therapy template on TheraPlatform.
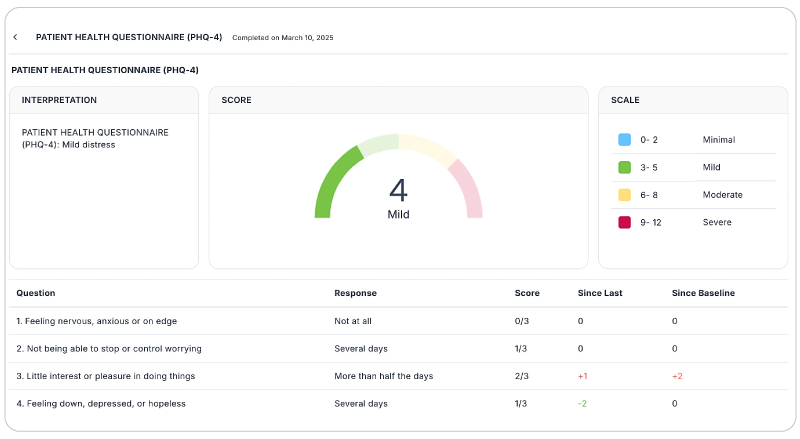
Save time with automatically scored outcome measures
Mental health therapists can use outcome measures to document progress, track a variety of key clinical indicators, helping providers make data-driven decisions, improve communication with clients, and improve client outcomes. Additionally, outcome measures help therapists adhere to compliance requirements and provide documentation needed to support reimbursement.
While outcome measures clearly provide benefits to both clients and therapists, they can be time-consuming, especially if clinicians score responses manually.
However, many aspects of outcome measures can be automated through an EHR like TheraPlatform:
- Sending measurements: Common assessments such as the PHQ-9 or GAD-7 can be automatically sent to clients and stored in their records or they can be scheduled on regular intervals.
- Auto scoring: TheraPlatform automatically scores and sums totals for common outcome measures.
- Report building and analysis: Results can be analyzed over time, with visual charts showing progress on rates of severity and session-to-session progress.
By regularly using these measures, therapists can gain valuable insights, tailor interventions, and improve client outcomes while demonstrating the effectiveness of their care without manual entry.
Empowering mental health therapists with PIE notes
Within the healthcare field effective documentation is essential for tracking client progress, ensuring continuity of care, and fostering professional collaboration. PIE notes offer a concise and structured approach to documentation, enabling therapists to capture the essence of each therapeutic session while maintaining clarity and efficiency.
By using PIE note documentation, therapists can streamline their note-taking processes, enhance communication among care providers, and ultimately provide higher-quality care to their clients. As the mental health field continues to evolve, embracing innovative and client-centered documentation practices like PIE notes will become increasingly crucial for therapists seeking to deliver exceptional services and achieve optimal treatment outcomes.
As mental health professionals, our commitment to providing compassionate and effective care extends far beyond the therapy room. By adopting a structured and meticulous approach to documentation, we not only enhance our own practice but also contribute to the broader advancement of the field. Each carefully crafted PIE note serves as a testament to our dedication, a record of the therapeutic journey we undertake alongside our clients.
Streamline your practice with One EHR
- Scheduling
- Flexible notes
- Template library
- Billing & payments
- Insurance claims
- Client portal
- Telehealth
- E-fax

Resources
TheraPlatform is an all-in-one EHR, practice management, and teletherapy software with AI-powered notes built for therapists to help them save time on admin tasks. It offers a 30-day risk-free trial with no credit card required and supports mental and behavioral health, SLPs, OTs, and PTs in group and solo practices.
Free resources for therapists
- Therapy resources and worksheets
- Therapy private practice courses
- Ultimate teletherapy ebook
- The Ultimate Insurance Billing Guide for Therapists
- The Ultimate Guide to Starting a Private Therapy Practice
- Mental health credentialing
- Insurance billing 101
- Practice management tools
- Behavioral Health tools
Free video classes for therapists
- Free on-demand insurance billing for therapist course
- Free mini video lessons to enhance your private practice
- 9 Admin tasks to automate in your private practice
References
Bipeta R. (2019). Legal and Ethical Aspects of Mental Health Care. Indian journal of psychological medicine, 41(2), 108–112. https://doi.org/10.4103/IJPSYM.IJPSYM_59_19
HIPAA privacy rule and sharing information related to ... US Department of health and human services. (n.d.). https://www.hhs.gov/sites/default/files/hipaa-privacy-rule-and-sharing-info-related-to-mental-health.pdf
Buckley-Womack, C., & Gidney, B. (1987). A new dimension in documentation: the PIE method. The Journal of neuroscience nursing : journal of the American Association of Neuroscience Nurses, 19(5), 256–260. https://doi.org/10.1097/01376517-198710000-00007
Medicaid Documentation for Mental Health Care Providers. Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services(n.d.). https://www.cms.gov/Medicare-Medicaid-Coordination/Fraud-Prevention/Medicaid-Integrity-Education/Downloads/docmatters-behavioralhealth-factsheet.pdf
FAQs about PIE notes
What are PIE notes and why are they used in therapy documentation?
PIE notes stand for Problem, Intervention, and Evaluation — a structured, concise format therapists use to document client sessions clearly and efficiently, helping track client concerns, actions taken, and progress over time.
How do PIE notes differ from traditional SOAP notes?
Unlike SOAP notes, which include four sections and can be more comprehensive, PIE notes focus on just three core elements: the client’s problem, the interventions used, and the evaluation of outcomes — making them more streamlined for many outpatient or private practice settings.
Can PIE notes be created and managed within an EMR like TheraPlatform?
Yes — EMR platforms such as TheraPlatform offer customizable templates, secure storage, and efficient workflows that help therapists create, store, and share PIE notes while saving time and improving documentation consistency.



